
In process development, scientists and engineers investigate the various options available for synthesizing, purifying, characterizing, and formulating the final product. At the early stages of idea generation, process simulation is primarily used for screening and evaluating potential projects in order to determine which ones to move forward with.įigure 42.1 Benefits from the use of computer aids. The typical stages of development and commercialization, and the activities associated with those stages, are shown in Figure 42.1.

The specific questions that must be evaluated and the level of accuracy of the answers depend upon the stage of development for a given product. The research results of this paper established a quick response, high efficiency, and flexible job-shop scheduling scheme for the aerospace complex components manufacturer, and lay a foundation for other multi-variety, single-piece and small-batch manufacturers to solve similar problems in the future.Chapter 42 Bioprocess Simulation and Schedulingĭoug Carmichael, Charles Siletti, Alexandros Koulouris and Demetri Petrides 42.1 The Purpose of Bioprocess Simulationīioprocess design and analysis attempts to answer questions such as the following: What are the required amounts of raw materials and utilities for manufacturing a certain amount of product per year? What is the required size of process equipment and supporting utilities? Can the product be manufactured in an existing facility or is a new plant required? What is the total capital investment for a new facility? What is the manufacturing cost? How long does a single batch take? What is the minimum time between consecutive batches? What is the demand for various resources (e.g., raw materials, labor, utilities, etc.) during the course of a batch? Which process steps or resources are the likely production bottlenecks? What process and equipment changes can increase throughput? What is the environmental impact of the process? Which design is the “best” among several plausible alternatives? The simulation results show that the model and algorithm in this work can effectively reduce energy consumption, shorten the production makespan and improve the utilization of various resources in the job shop. Finally, the Plant Simulation is used to verify the practicability of the proposed energy-efficient model and algorithm. The results show that the proposed algorithm is a very competitive algorithm for this real-world instance. Then, a comparative experiment of the proposed algorithm and other famous optimization algorithms including ABC, MOBA, NSGA-II, as well as heuristic scheduling methods including RANDOM+LPP and RANDOM+SPT is designed to verify the energy-saving effect of the proposed model and the feasibility of the algorithm. In this way, the Pareto optimal solution set is obtained. Moreover, the parameter setting of the proposed algorithm is calibrated by a new assessment metrics ASQ and the DOE Taguchi method. Specifically, a multi-objective process tree algorithm is introduced to address the poor quality of random initial solutions, and the crossover and mutation are designed in the global search of employed bees to improve the population diversity. A novel improved crossover artificial bee colony algorithm is presented to cope with the combinatorial optimization problem in the model. To handle the issues of low production efficiency, high energy consumption and processing cost in the job-shop, an aerospace complex components lot-splitting scheduling model is formulated with the optimization objectives of total energy consumption, makespan, and processing cost for the first time. This paper focuses on a real case energy-efficient scheduling problem for aerospace complex components in a flexible job-shop with complex processes.

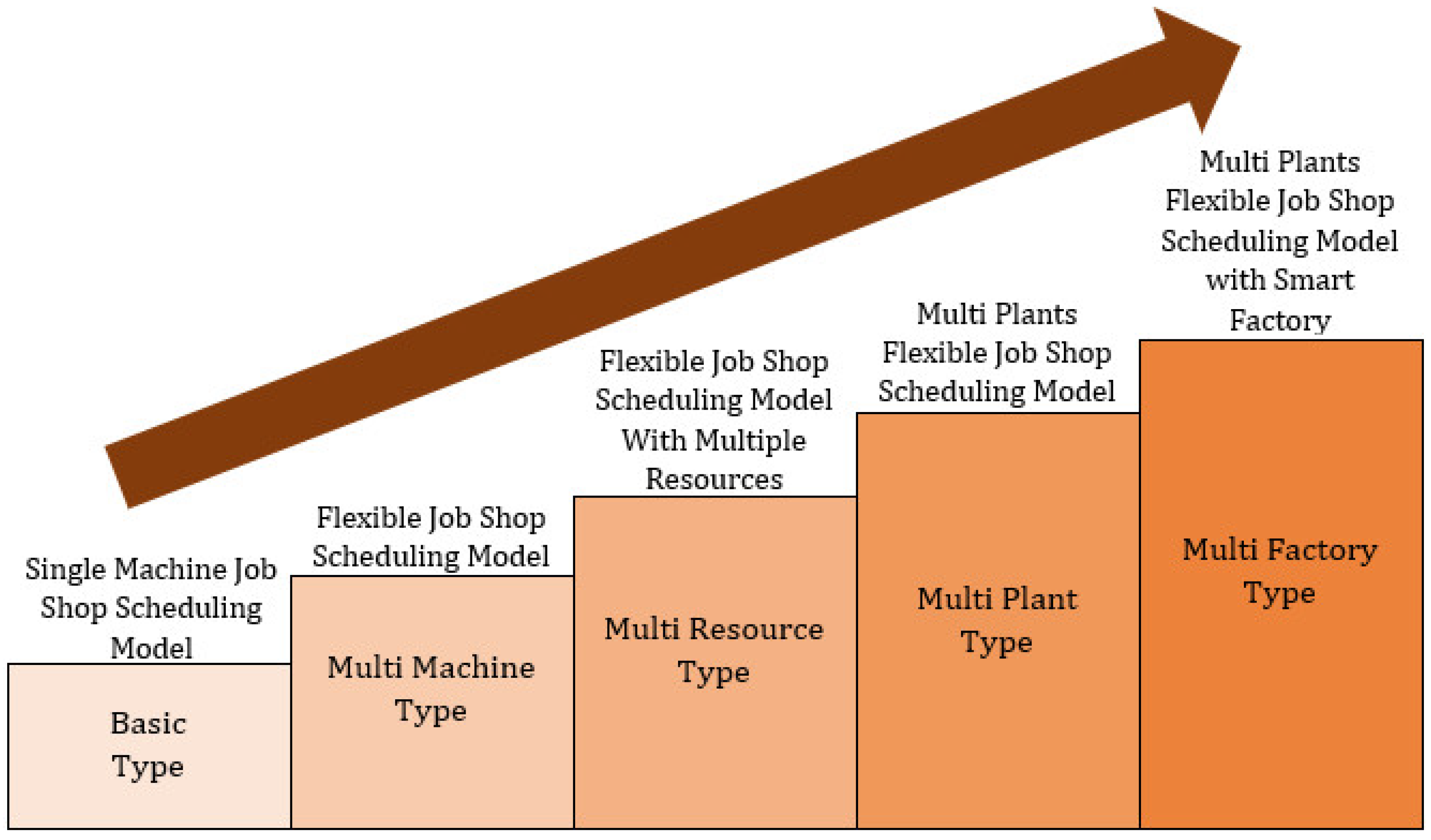
Energy-Efficient Scheduling of Flexible Job Shops with Complex Processes: A Case Study for the Aerospace Industry Complex Components in China Journal of Industrial Information Integration ( IF 10.063), Pub Date : , DOI: 10.1016/j.jii.2021.100293 Xingyu Jiang, Zhiqing Tian, Weijun Liu, Yingqi Suo, Keqiang Chen, Xiaowen Xu, Zhiwu LiĪs an effective means to reduce enterprise energy consumption, job-shop scheduling has received extensive attention in the industry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
